This task shows how to provision Control Plane and Workload Certificates with an external Certificate Authority using cert-manager. cert-manager is a x509 certificate operator for Kubernetes that supports a number of Issuers, representing Certificate Authorities that can sign certificates. The istio-csr project installs an agent that is responsible for verifying incoming certificate signing requests from Istio mesh workloads, and signs them through cert-manager via a configured Issuer.
Install cert-manager
First, cert-manager must be installed on the cluster using your preferred method.
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo update
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
helm install -n cert-manager cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager --set installCRDs=true
Verify the cert-manager deployments have successfully rolled-out.
for i in cert-manager cert-manager-cainjector cert-manager-webhook; \
do kubectl rollout status deploy/$i -n cert-manager; done
Configure cert-manager
An Issuer must be created
in the istio-system namespace to sign Istiod and mesh workload certificates.
We will use a SelfSigned Issuer,
though any supported Issuer can be used.
Note that publicly trusted certificates are strongly discouraged from being used, including ACME certificates.
kubectl create namespace istio-system
kubectl apply -n istio-system -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: selfsigned
spec:
selfSigned: {}
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: istio-ca
spec:
isCA: true
duration: 2160h # 90d
secretName: istio-ca
commonName: istio-ca
subject:
organizations:
- cert-manager
issuerRef:
name: selfsigned
kind: Issuer
group: cert-manager.io
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: istio-ca
spec:
ca:
secretName: istio-ca
EOF
Verify the “istio-ca” and “selfsigned” issuers are present and report READY=True:
kubectl get issuers -n istio-system
Once the issuers have become ready,
istio-csr can be installed into the
cluster.
Install istio-csr
helm install -n cert-manager cert-manager-istio-csr jetstack/cert-manager-istio-csr
Verify the istio-csr deployment has successfully rolled-out.
kubectl rollout status deploy/cert-manager-istio-csr -n cert-manager
Certificates “istio-ca” and “istiod” should be present and report READY=True.
kubectl get certificates -n istio-system
Install Istio
Istio must be configured to use cert-manager as the CA server for both workload and Istio control plane components. The following configuration uses the IstioOperator resource to install Istio with cert-manager integration:
getmesh istioctl install -y -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:
namespace: istio-system
spec:
values:
global:
# Changes the certificate provider to Cert Manager istio-csr
caAddress: cert-manager-istio-csr.cert-manager.svc:443
components:
pilot:
k8s:
env:
# Disables istiod CA Sever functionality
- name: ENABLE_CA_SERVER
value: "false"
overlays:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: istiod
patches:
# Mounts istiod serving and webhook certificates from Secret
- path: spec.template.spec.containers.[name:discovery].args[-1]
value: "--tlsCertFile=/etc/cert-manager/tls/tls.crt"
- path: spec.template.spec.containers.[name:discovery].args[-1]
value: "--tlsKeyFile=/etc/cert-manager/tls/tls.key"
- path: spec.template.spec.containers.[name:discovery].args[-1]
value: "--caCertFile=/etc/cert-manager/ca/root-cert.pem"
- path: spec.template.spec.containers.[name:discovery].volumeMounts[-1]
value:
name: cert-manager
mountPath: "/etc/cert-manager/tls"
readOnly: true
- path: spec.template.spec.containers.[name:discovery].volumeMounts[-1]
value:
name: ca-root-cert
mountPath: "/etc/cert-manager/ca"
readOnly: true
- path: spec.template.spec.volumes[-1]
value:
name: cert-manager
secret:
secretName: istiod-tls
- path: spec.template.spec.volumes[-1]
value:
name: ca-root-cert
configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: istio-ca-root-cert
EOF
The installation should complete, and the Istio control plane should become in a ready state.
kubectl get pods -n istio-system
Test mTLS
All workload certificates will now be requested through cert-manager using the configured Issuer. Let’s run an example workload to test mTLS. First, create a namespace and configure it for automatic sidecar injection:
kubectl create ns foo
kubectl label ns/foo istio-injection=enabled
Run the sample sleep and httpbin workloads.
ISTIO_VERSION=1.11
kubectl apply -n foo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-$ISTIO_VERSION/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
kubectl apply -n foo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-$ISTIO_VERSION/samples/httpbin/httpbin.yaml
Verify the sleep and httpbin deployments have successfully rolled-out.
for i in sleep httpbin; do kubectl rollout status -n foo deploy/$i; done
Verify the sidecar proxy was injected for each workload. Each workload pod should
show 2/2 containers are READY.
for i in sleep httpbin; do kubectl get po -n foo -l app=$i; done
By default, Istio configures destination workloads using PERMISSIVE mode. This
mode means a service can accept both plain text and mTLS connections. To ensure
mTLS is being used between sleep and httpbin workloads, set the mode to STRICT
for namespace “foo”.
kubectl apply -n foo -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: PeerAuthentication
metadata:
name: "default"
spec:
mtls:
mode: STRICT
EOF
Test mTLS from the sleep pod to the httpbin pod.
kubectl -n foo exec -it deploy/sleep -c sleep -- curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{http_code}\n' http://httpbin.foo:8000/headers
You should receive an 200 response code.
Visualize mTLS
Optionally, you can run Kiali to visualize the mTLS connections.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-$ISTIO_VERSION/samples/addons/prometheus.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-$ISTIO_VERSION/samples/addons/kiali.yaml
Verify the Kiali and Prometheus deployments successfully rolled-out.
for i in prometheus kiali; do kubectl rollout status -n istio-system deploy/$i; done
Open the Kiali dashboard.
istioctl dashboard kiali
Navigate to Workloads > Namespace:foo > httpbin. You should see the connection graph with padlocks to indicate mTLS is being used. If the graph is empty, adjust the “traffic metrics per refresh” dropdown list in the upper right-hand corner or regenerate connections.
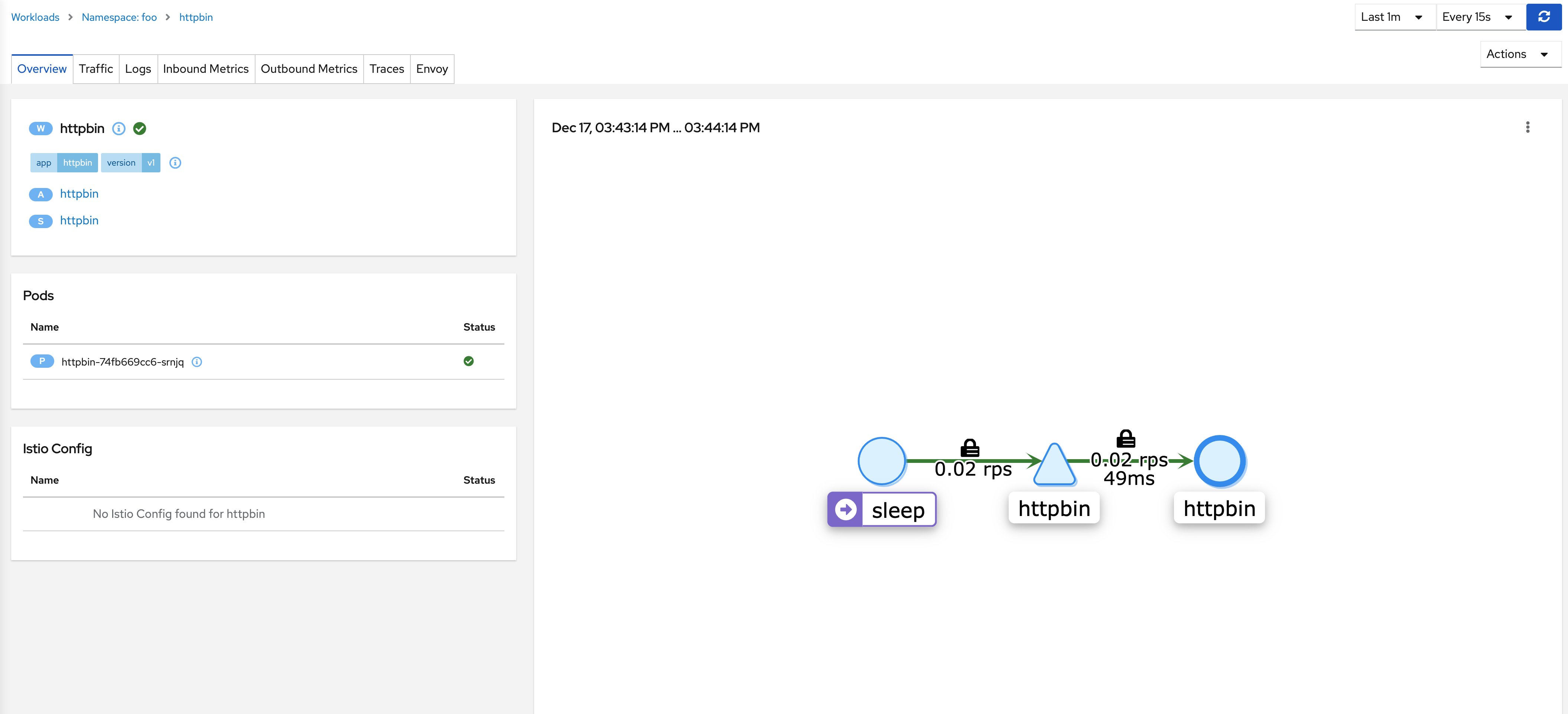
Congratulations, you successfully configured Istio to use cert-manager as a CA for mesh mTLS authentication.